Waterproof Cooler Bags: A Deep Dive into Durability and Waterproofing
In the realm of outdoor activities, picnics, and even daily commuting, waterproof cooler bags have emerged as an essential accessory. While their primary function is to maintain the temperature of stored items, their durability and waterproofing capabilities are equally critical. This article delves into the technical aspects that make these bags both long-lasting and resistant to water.
1. The Importance of Durability and Waterproofing
A cooler bag's lifespan and its ability to protect its contents from external moisture are paramount. Users not only expect their bags to withstand regular wear and tear but also to offer consistent protection from water, ensuring the safety and freshness of the stored items.

2. Materials Matter: The Backbone of Durability
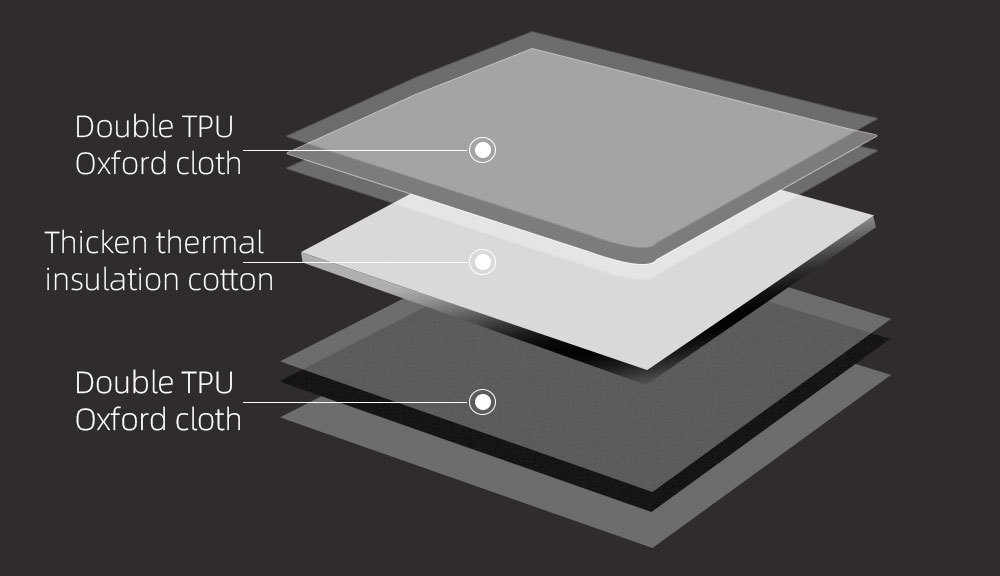
High-Density Fabrics: Fabrics like nylon and polyester, known for their strength and resilience, are commonly used. Their tight weave ensures minimal wear over time.
Reinforced Stitching: Critical stress points, such as handles and zippers, often feature reinforced stitching to prevent tearing and enhance longevity.
UV Resistance: Materials that resist UV degradation prevent the bag from becoming brittle or discolored when exposed to sunlight.

3. Waterproofing Techniques: Beyond Just Materials
Tightly Woven Fabrics: While the fabric itself plays a role, the tightness of the weave can prevent water penetration to a significant extent.
Waterproof Linings: Internal linings, often made of materials like TPU or PVC, provide an additional layer of moisture protection.
Sealed Seams: One of the most common entry points for water is the seams. Using techniques like seam taping or welding ensures that these potential weak points are watertight.
Water-Resistant Zippers: Standard zippers can allow water ingress. Water-resistant zippers, often coated or made from materials that repel water, are essential for a truly waterproof bag.

4. Testing Durability and Waterproofing
To ensure that a cooler bag meets the required standards, rigorous testing is essential.
Abrasion Testing: This tests the fabric's resistance to wear and tear by simulating repeated rubbing or scraping.
Hydrostatic Pressure Test: By subjecting the bag to increasing levels of water pressure, this test determines the point at which water begins to seep through.
Submersion Test: A straightforward test where the bag is submerged to check for any water ingress.